▸ Therapeutic Endoscopy : ESD and EMR
 Two types of therapeutic endoscopy can be done for removing gastric cancer, one is “Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)”, the other is “Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD)”. EMR is usually performed with a high-frequency steel snare which is used to strangulate and resect the mucosal lesion in the stomach. ESD is employed with using a unique knife (usually insulation-tipped) to dissect the gastric submucosa from the proper muscle layer. The advantage of using EMR is that it can be done in short time, but its resection is limited to the size of elctrosurgical snare. The dissected portion of ESD is not limited to the size of lesion as it is using a unique knife.
Two types of therapeutic endoscopy can be done for removing gastric cancer, one is “Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)”, the other is “Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD)”. EMR is usually performed with a high-frequency steel snare which is used to strangulate and resect the mucosal lesion in the stomach. ESD is employed with using a unique knife (usually insulation-tipped) to dissect the gastric submucosa from the proper muscle layer. The advantage of using EMR is that it can be done in short time, but its resection is limited to the size of elctrosurgical snare. The dissected portion of ESD is not limited to the size of lesion as it is using a unique knife.
| 1 | EMR ( Endoscopic Mcosal Resection) |
| For removal of early gastric cancer (~ 2 cm in size) |
| 2 | ESD ( Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ) |
| Theoretically, ESD is not limited to the tissue size. The larger lesion can be completely dissect ed and removed. |
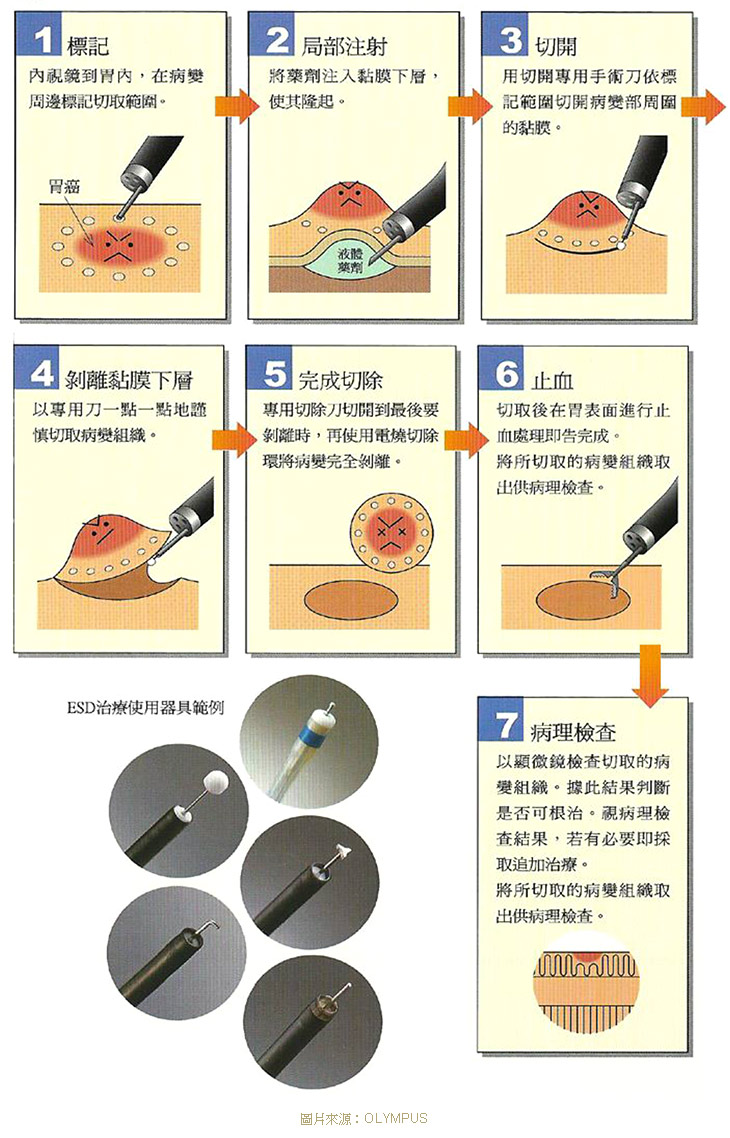
▸ Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ( ESD )
▸ Endoscopic Mucosal ( EMR )
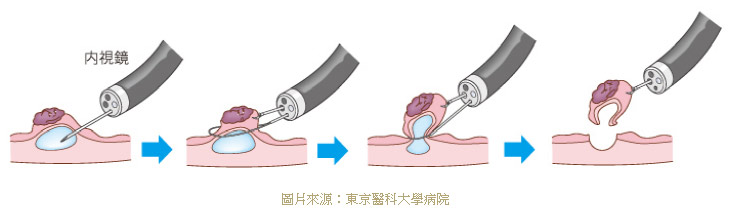
| 1 | Observe the center of a suspected lesion: immediately remove it by EMR if it is more likely to be cancerous. |
| 2 | Inject the saline into the submucosa of the lesion so that an elevation is founded with the lesion at its highest point |
| 3 | Put the snare around the elevation. Strangulate the elevation until resistance is felt |
| 4 | Activate the electrosurgical unit to resect the lesion. |
▸ ESD Q&A
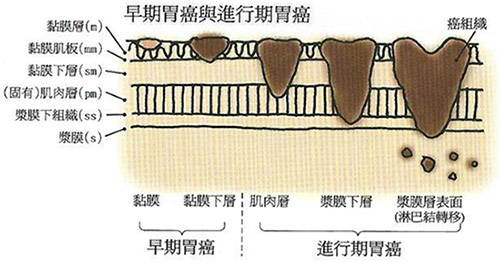
What kind of gastric cancer can be treated with endoscopy?
ESD can be performed for the treatment of early diagnosed gastric cancer which is defined as invasive gastric cancer that invades no more deeply than the submucosa. Based on the Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines published by Japanese Gastric Cancer Association, ESD can be applied if the following condition met. Firstly, removal of gastric cancer often require removing a quite large portion. Secondly, there is no possibility of lymph node metastasis. Above guidelines can be further defined as below standards:
| 1 | 1. Intramucosal carcinoma: Cancer cells are only found in the top layers of the gastric lining called the mucosa. |
| 2 | 2.Differentiated carcinoma: The gastric mucosa consists of mature cancer cells arrayed in it |
| 3 | 3.The cancer is less than 2 cm in size |
| 4 | 4.No complicated stomach ulcer |
Patients with gastric cancer which met above standards can be treated with endoscopy. As to the size of gastric cancer, it is reported that ESD can apply to cancers larger than 2 cm in many clinical cases.
▸ Why to remove the lesion completely?
 The resected tissue can be examined under the microscope for diagnostic purposes (so-called " pathological diagnosis " ). It is necessary to completely remove the lesion for accurate pathological diagnosis even if the low risk of lymph node metastasis is diagnosed. The endoscopy can be used for examination of deep layer of the gastric mucosa in order to check if cancer cells have invaded blood vessels and lymph-vessel. A follow-up treatment can be done if necessary.
The resected tissue can be examined under the microscope for diagnostic purposes (so-called " pathological diagnosis " ). It is necessary to completely remove the lesion for accurate pathological diagnosis even if the low risk of lymph node metastasis is diagnosed. The endoscopy can be used for examination of deep layer of the gastric mucosa in order to check if cancer cells have invaded blood vessels and lymph-vessel. A follow-up treatment can be done if necessary.
▸ What things should be taken into consideration during the ESD treatment?
ESD treatment may take a long time due to different morphology of the lesion; it may also cause a high risk of complications, therefore, it is necessary to see the physician and get their complete advice before the treatment.
The possible complications caused by ESD treatment
- Gastrointestinal bleeding (Also known as gastrointestinal hemorrhage)
- Gastric perforation
- Sedatives may cause adverse effects
If above complications occurred, the proper measures must be taken promptly. Althoughmost cases of gastrointestinal bleeding and gastric perforation can be managed through endoscopy, some cases may require surgical operations. Please see the physician and get their advice about the complications. Please feel free to consult your physician for any further questions or concerns. Since different clinics take different measures, please contact your clinic directly for ESD details.